While there’s nothing new in malicious advertisers being used as vectors of online attacks and fraud, cyber criminals are paying more attention on malvertising as a means to perpetrate advanced persistent threats.
Researchers from security firm Invincea have found that various groups are now growing in number who resort to malvertising to intercept networks of large organizations and companies, including your favorite social networks. Although the form of attacks derive from the not so sophisticated origins, the actual attacks being launched are of higher levels and more complex to detect.
The malvertising schemes are mostly state-sponsored, meaning that from where the attacks came from, the attackers are getting their financial resources from the government, thus they are considered legitimate in that territory and could hardly be sanctioned through the court of law.
These state sponsored attacks are believed to be a form of retribution to opponent states as governments worldwide are launching massive cyber attacks against each other. They are mostly those with enough resources to carry out the attacks.
Invincea also said the attacks employed were new in that the level of aggressiveness has never been known before.
Amid war of states in the cyber space, the ones who are mostly impacted the most are the netizens who might not be fully aware of what is going on. The targets are also very specific, as opposed to indiscriminate attacks from traditional malvertising campaigns.
How does this new attack scheme work? Malvertisers lure lead users to third party sites using fraudulent schemes. First, they would manipulate an advertising network and redirect the network’s visitors to a third party site that hosts malicious ads. These kinds of sites have exploit kits and malware lurking in its corners ready to infect the computer of an unsuspecting user.
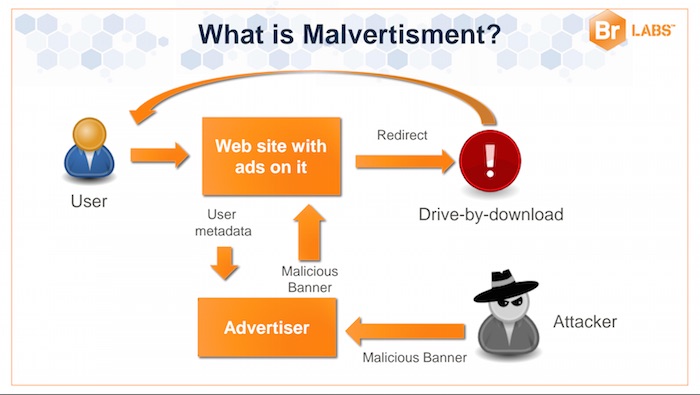
But as stated above, the new malvertising scheme uses different techniques compared to traditional campaigns. These malvertising targets specific users based on their versions of Flash software, operating system, cookies, interest and java plugin so as to identify which sector or organization they belong.
To make their scheme look legit, these malvertisers also participate in ad bidding in order to place their malicious ads on sites that attract large volumes of visitors and clicks. The more the visitors who would potentially click on their ads, the more effective their campaign.
Why do these ads proliferate and thrive even if the sites hosting them know that they lead to malicious pages? Well, because of profit. One indication to tell a malvertisement is that it offers a product under terms that are too good to be real.
Disclosure: We might earn commission from qualifying purchases. The commission help keep the rest of my content free, so thank you!




Rachella Smith says
Thanks for the wonderful post about new malvertising scheme uses different techniques compared to traditional campaigns.