Most probably you already know that flash memory is better than spinning disks. In the data storage market, flash memory enjoys more popularity than traditional hard drives. And as flash-based memory devices continue to dominate the market, hard disk drives are experiencing a bit of a slump.
But is flash memory the best choice for all users? When it comes to picking a memory device that works best for you, you need to take several things into account. You should think about your budget, storage space you need, as well as potential physical damage and data loss. Moreover, you should also consider whether you’ll be carrying the device everywhere to back up and transfer files. Once you figure out your specific data storage needs, the next step is to evaluate the pros and cons of different storage devices. Since flash memory technology is comparatively new, you will also need need to be carefull with the storage. Recovering data from Flash storage is not a DIY job and a specialist might be needed for recovering data from devices such as Silicon Power and for WD Data Recovery. With that in mind, here’s some useful information to help you head in the right direction.
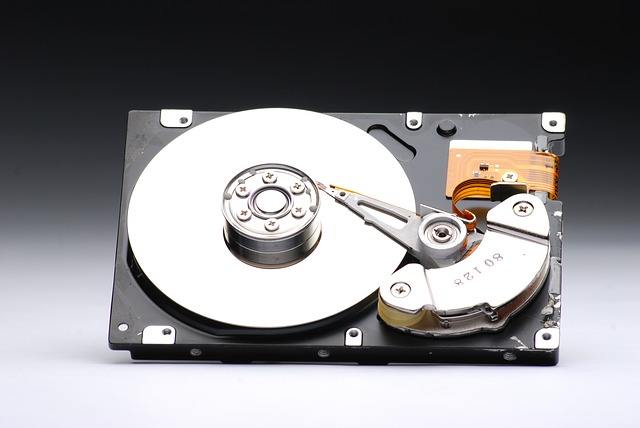

When it comes to storage media, the main type of memory includes flash and hard disk. Although HDD and flash memory differs from each other, they do share some similarity as well. For instance, both HDD and the flash drive use non-volatile memory that retains its data even without receiving electrical power. As far as the difference is concerned, flash memory is a solid-state memory chip with no moving parts while hard disk consists of spinning platters. Now let’s take a closer look at these two memory types to get a better idea.
Flash Memory
Flash memory uses memory chips that can keep data intact even without power. It means that you won’t lose data even if the power goes out or the disk is turned off. There are multiple flash-based storage devices in the market including USB sticks and enterprise all-flash arrays. This electrically programmable memory can write data and performs random I/O operations at high-speed. The flash-based storage devices use memory cells to store data. To write new data, the flash memory erases the cells with previously written data. The flash memory chip can be either NOR or NAND. The devices with the NOR gate interface can have 10,000 to 1,000,000 write/erase cycles. The faster NAND gate, on the other hand, has about 100,000 writes/erase cycles. Flash storage is of three basic types— SLC (Single Level Cell) MLC (Multi-Level Cell) and TLC (Triple Level Cell). It is noteworthy here that flash is SSD, but not all SSD is Flash.
Hard Drive
A hard disk is an electromechanical data storage device that uses magnetic storage. Similar to flash memory, a hard disk drive is also non-volatile. It is a storage device that maintains data integrity even when the computer is switched off. However, this device consists of a mechanical read/write head and spinning metal platters that have a magnetic coating for storing data. In a hard disk drive, the magnetic disks, also known as “platters” is turned on by a motor and arms scan the spinning disks to read and write data. This traditional storage unit doesn’t deteriorate through rewrites and has a larger amount of storage space.
HDD vs. Flash
Flash memory is commonly found in USB flash drives, MP3 players, digital cameras, and solid-state drives. It differs from the hard drive in terms of size, cost, longevity, operating speed, and reliability. The main advantage of using a flash memory device like an SSD is speed. The storage devices that run on flash memory are faster than traditional HDDs. This means that if your laptop or computer has an SSD, it will boot within seconds. Likewise, flash drives can quickly copy and transfer files from one computer to another. A hard drive, on the other hand, can become slow due to fragmentation. As more data is stored on the HDD, it gets scattered on the platter causing fragmentation.
Flash memory has no moving parts which make flash devices more portable and less vulnerable to mechanical damage. Devices like flash drive allow carrying data wherever you go and because of lack of moving parts, there are fewer chances of damage and data loss. This feature also makes flash memory devices more durable. In contracts to flash drives, hard drives are mechanical and more vulnerable to damage. Also, the head of the HDD keeps constantly moving over the metal platters that causes wear and tear.
Flash memory enjoys more popularity but this doesn’t mean that it’s a perfect technology. Flash drives and SSDs are less vulnerable to data loss than HDDs. However, flash devices can wear out and may get damaged due to various reasons. The tunnel oxide layer of the flash device can degrade, casing flash memory wear issues. Moreover, even the most reliable devices like Silicon Power SSD can suffer data loss due to sudden power loss or physical damage.
Another downside of flash memory is the cost. As compared to HDDs, flash devices like solid-state drives are far more expensive. For those who want to store a huge volume of data, a hard disk can be an economical choice. HDDs also have a higher read/write cycle.