After the leakage of exploit kits from the Hacking Team’s servers, cyber attackers have taken advantage of the stolen information to inject the Towelroot exploit kit to Android devices, marking yet another spike in the exponential growth of the ransomware threat landscape.
Security researchers at Blue Coat Labs revealed that the attackers behind what is called the Dogspectus ransomware are working to furtively install the malware in mobile devices running the Android operating system using a variety of vulnerabilities data contained in the Hacking Team’s servers. In addition to the ransomware, the cyber attackers are also launching malvertising attacks against Android users.
The attack vectors were detected after the Blue Coat Labs security experts conducted a test on an old Samsung tab that runs the Cyanogenmod 10 version of Android 4.2.2. Prior to the ransomware attack, the attackers injected a malicious Javascript through malvertising onto the device. It was hard for ordinary anti-malware tools to detect the tactic, much less for Android users, because the exploit kit installs the malicious apps in the mobile device even without requiring interaction with the user.
What adds to the furtive manner with which the malware is installed in Android devices is the absence of the dialog box that would ask permission for the application’s installation in the device, meaning the malware is downloaded in the background.
The attack stems from the exploit kit that slipped off from the servers of Hacking Team – a Milan, Italy-based vendor of exploits whose databases fell prey to a breach in 2015, unloading a treasure trove of zero-day vulnerabilities.
How the malware works
It is not clear when exactly the attack has kicked off, but Blue Coat researchers say the attacks have started before mid-February this year and already hundreds of mobile devices have been linked to the exploit kit’s command and control servers.
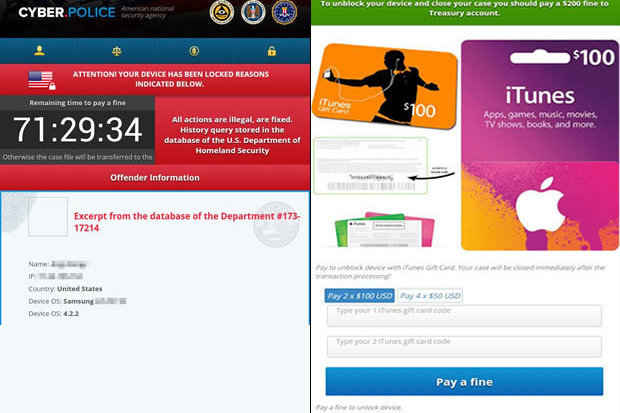
The Dogspectus ransomware disguises as a U.S. law enforcement agency and snoops on the browsing behavior of the victim. Unlike other ransomware that encrypts files, this one only locks the device and kills all applications installed in the device.
How to remove the ransomware
The attackers behind the Dogspectus ransomware might have committed a major blunder in the way they ask for ransom payment from the victims. This form of ransomware does not demand ransom payment in virtual currency like Bitcoin. Instead the victims are asked to pay Apple iTunes gift card codes worth $200.
Unlike in the iPhone encryption case, Apple may help the FBI trace down the attacker by monitoring the gift cards paid to the criminals and help solve cases involving the Dogspectus ransomware. Better yet, Android users who may be hit by this ransomware can remove the malware from their device by performing the factory reset option.